Chapter 1: Introduction to Project Management

Meet the team
We are Emma, Leon, Gabby & Sal and we’re building a product together called ‘GranGroceries’. It’s a grocery delivery service for elderly people. We’ll be dividing the tasks to make sure this project becomes a success.
Over the next hour and a half, you’ll discover together with us what it means to be a Project Manager. Step by step you will get to know the most sought after processes, skills and concepts within Project Management. This way you’ll be able to apply them to any future project. We will walk you through the project management processes and teach you the skills and concepts of project management that can be applied to any project.
Curious? Let’s start.”


Activity 1: What is a project?
Each time you planned what clothes to pack for a holiday, scheduled a time for your group of friends to get together, prepared a presentation, or built a paper airplane with your team, you were participating in various aspects of project management.”

Activity 2: Key Roles in Project Management

Activity 3: Project Management Processes
- The Initiating process is the beginning of the project. During this process, project stakeholders are identified and a project manager is selected. Project goals and objectives are defined and authorization is obtained to proceed with the project.
- During the Planning process, the project plan is created. The project manager and team members define the activities needed to complete the final product, service or result. They also determine what staff and resources are needed, establish the timeline and available budget for the project. The planning process is very important to the overall success of the project. Without careful planning, a project manager and project team may find it very difficult to achieve project success.
- Executing is the process of working through the project plan. The executing stage involves performing the activities outlined during the planning process.
- Monitoring and Controlling occurs throughout the entire project. Monitoring and controlling involves ensuring that all the activities in the project plan are completed on time and within budget, as well as addressing any changes necessary to successfully achieve the project goals.
- In the Closing process, project goals are delivered. Final administrative work is completed and lessons learned are captured to improve future projects. The closing process involves taking the time to celebrate the team’s successes along the way toward completion of the project.
Help us to take the right steps in the project by dragging them into the right order.”
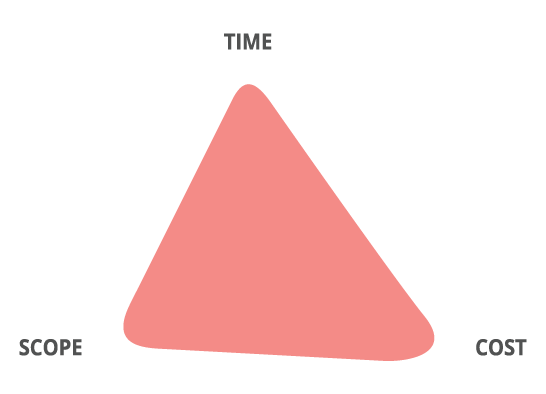
Activity 4: The Triple Constraints
Go to the next Chapter
Chapter 2: Initiating the project
Key terminology
Click on the words to expand the window and understand what they mean:
Acceptance criteria:
Activity:
Assumption:
Closing process:
Communication management:
A component of the project, program, or portfolio management plan that describes how, when, and by whom information about the project will be administered and disseminated.
Constraint:
Deliverable:
Executing process:
Initiating process:
Lessons learned:
Milestone:
Milestone planning:
Monitoring and controlling process:
Planning process:
Project:
Project Charter:
Project Management
Project Manager
Project Schedule
An output of a schedule model that presents linked activities with planned dates, durations, milestones, and resources.
Project Team
A set of individuals who support the project manager in performing the work of the project to achieve its objectives.
Scope:
Scope creep:
Sponsor:
Stakeholder:
Stakeholder register
Resource
A team member or any physical item needed to complete the project.
Risk:
An uncertain event or condition that, if it occurs, has a positive or negative effect on one or more of the project objectives.
Work Breakdown Structure (WBS):
A hierarchical decomposition of the total scope of work to be carried out by the project team to accomplish the project objectives and create the required deliverables.
